
International Payment Methods in Import and Export Coffee – With the current trend of globalization, trading, trading, and buying and selling Coffee are gradually becoming more accessible and more convenient.
So how can two organizations or individuals in two territories and countries at a far distance from each other be able to buy, sell and make payment transactions quickly?
Besides that, Coffee is an important and key export item of Vietnam. Vietnamese coffee products are increasingly showing their strength in the world coffee market. Therefore, coffee export procedures are interested in many businesses.
Please read the article below to understand more about international payment methods!
The concept of international payment in coffee purchasing
International payment means the performance of payment obligations and monetary benefits arising based on economic and non-economic activities between organizations and individuals of this country and organizations and individuals of other countries or between a government and an international organization, through relationships between banks of the countries concerned.
Features of international payments
- International laws and practices govern international payment activities.
International payment activities involve entities in two or more countries.
Therefore, when participating in international payment activities, entities are not only subject to national laws but also must comply with international regulations—compliance with international legal documents.
The International Chamber of Commerce promulgates UCP, URC, and INCOTERMS… creating an equal and fair legal framework for entities when participating in international trade and payment activities, avoiding unfortunate misunderstandings occurring…
- International payment activities are done mainly through the banking system.
Except for a minimal amount of import and export Coffee bought and sold through unofficial channels, most of a country’s import and export turnover is reflected in the global payment turnover of the commercial banking system.
In practice, exporters and importers are not allowed to make payments directly to each other but, by law, must make payments through the banking system.
The payment via Bank ensures that payments are made safely, quickly, and efficiently.
- In international payments, cash is seldom used directly but rather using amount.
Means commonly used in international payments such as drafts, promissory notes, and checks.
- In international payments, at least one of the two parties is involved in a foreign currency.
Due to the involvement of foreign currencies, international payment activities will be directly affected by the exchange rate and the management of foreign exchange reserves of the country.
- The language used in international payments is mainly English.
- Dispute settlement is mainly by international law.
The role of international payment methods in purchasing coffee
- For the economy: International payments contribute to the expansion and promotion of external economic relations, strengthen the financial position of each country in the international market, and create a bridge between countries in the economic relationship. Payment.
- For businesses: International payment serves the payment needs of companies in the international Coffee purchase and sale activities.
- For commercial banks: International payment generates service revenue and promotes the development of other activities of the Bank.

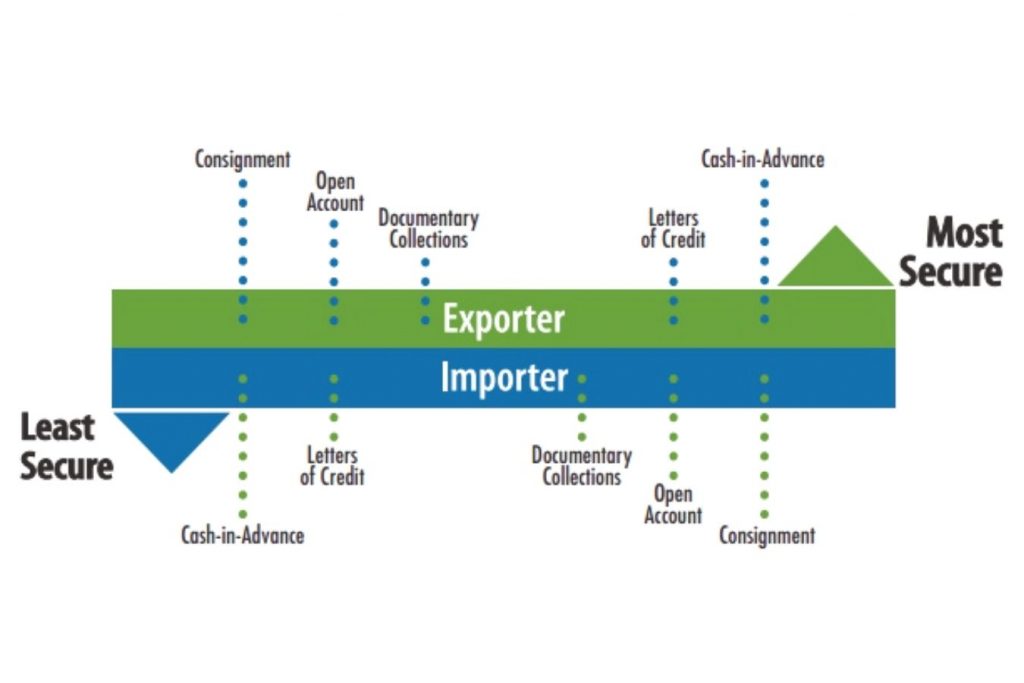
Basic international payment methods for Coffee Importer and Exporter
1. Open Account Method
Concept:
Remittance is a method in which a customer (remittance requester) requests their bank to transfer a certain amount of money to another person (the beneficiary) in a particular location using a money transfer specified by the customer.
Characteristic:
- It is a payment method without the involvement of the Bank with the function of opening an account and collecting money for bookkeepers.
- Only open a single-margin book, not a double-margin book. If the person being recorded opens the book for monitoring, that book has no settlement value between the two parties.
- From the point of view of collecting money, this method has only two participants: the bookkeeper and the person being recorded.
- The price of Coffee stated in the underlying contract of the bookkeeping method is usually higher than the price of the Coffee Products stated in the underlying agreement upon immediate payment.
- The bookkeeping payment method is essentially an import financing method so that the risk will be on the person being recorded.
Participating parties:
Exporters and importers only. The Bank only acts as the account opening party and makes payments based on the agreed payment period by the importing party to the exporting party.
Implementation process:
- The exporting party delivers the coffee products and sends the documents to the importing party to receive the coffee
- The exporting party debits the account and reports the debt directly to the importer
- Periodic payment (monthly, quarterly, or semi-annual) the importer transfers money through the payment bank to the exporter or pays by check.
When should the book payment method be used?
- The two parties have a steady trading relationship with a small quantity and have mutual trust.
- The exporting party sends the coffee to the importer or a distribution agent in a foreign country.
- Pay for service fees such as freight, insurance, postage, commissions, escrow fees, loan interest, or return on investment.
- Used in processing method
- This method is only beneficial to the person being recorded
Points to note:
- There are no international laws and practices governing the method of bookkeeping payments. When applying, it is necessary to use the country’s national law where the ledger is opened and the correspondent banking agreement between the two banks (if any).
- It is necessary to specify the currency to be debited on the ledger, the currency of payment, the money transfer method, and the sanctions for late, missing, or non-payment.
- In this method, the exporter opens an account (opens a book), and the importer does not open a parallel text. If the book is opened, it will only have monitoring value, not payment value.
2. Collection method
Concept:
A collection is a form of payment after the exporter sends the coffee to the importer and sends documents to his bank to collect money from the importer’s Bank.
The required collection documents are financial and commercial. This is a method where the role of the Bank is prominent, ensuring the safety of both import and export parties.
- Financial documents: drafts, promissory notes, checks, or other documents related to the purpose of payment.
- Commercial documents: Invoices, bills of lading, documents of title, or any document that is not a financial document.
Characteristic:
Collection methods include two types:
- A clean collection is the collection of only financial documents without commercial documents.
- Documentary collection collects commercial and financial documents or commercial documents without financial records.
Participating parties:
- The principal (Principal): is the person who authorizes the collection of collection transactions for the Bank, usually identical to the exporter or the beneficiary.
- Remitting Bank: is the Bank representing the nominated collector. This Bank is obliged to receive documents from the collection instructor according to the collector’s conditions. When receiving the documents like that, money for them will be transferred like that—usually identified with the Bank serving the exporter.
- Presenting Bank: is the Bank in the importing country which transfers the collection documents to the importer following the collection instructions.
- Collection bank: is the Bank that represents the payer. Any bank involved in a collection but not a forwarding bank is generally understood to mean the presenting Bank. If the exporter’s Bank does not specify the information, this Bank may be appointed by the transferring bank.
- Drawee: is the person presented with the documents following the collection instructions, usually identical to the importer.
2.1 Method of smooth collection
Implementation process:
- The exporting party delivers coffee products and sends documents to the importing party.
- Draw drafts and send collection requests to the exporting party’s Bank for collection from the foreign importing Bank.
- The exporter’s Bank transfers the bill of exchange and collects instructions to the importer’s bank in a foreign country.
- The collecting Bank presents the draft following the collection instructions to the drawee.
- The payer conducts the transaction or accepts the bill of exchange.
- The collecting Bank transfers money or an accepted draft to the sending Bank.
- The Bank transfers the accepted payment or draft to the exporter.
When should you use the smooth collection payment method?
- It should be used if the beneficiary and the payer trust each other, as the Bank is only an intermediary for collection.
- The method of smooth collection is rarely used in commercial payments, usually only applied in payment for commercial services such as collecting electricity and water bills, etc.
Points to note:
- This method is rarely used because it does not guarantee the interests of both parties. Because the Bank only plays an intermediary role in payment because the goods documents have been delivered to the importer, the correspondent bank cannot control importers. Specifically, the Bank will not be responsible in case of non-collection, insufficient collection, or untimely collection.
- Therefore, the exporter should only apply this method to have a long-term relationship and trust the importer.
- To limit risks, in the primary contract, the two parties need to agree on a specific time to pay or to accept payment immediately after the Bank presents the payment instrument. If you pay late, you will be penalized for late payment.
- The collection instruction must also stipulate similar sanctions provisions such as the payer, insufficient payment, illegal or unreasonable reasons to refuse payment, etc.
- This method is often used to pay fees or collect checks between banks.
2.2 Method of asking for collection with documents
In this method, to prevent and avoid the risk that the importer takes over the exporter’s capital, makes a late payment, lacks, or even refuses to pay, the seller often entrusts the Bank to act on their behalf.
Processing documents for importers with the condition that payment for documents (Documents against Payment – D/P) or acceptance of payment for documents (Documents against Acceptance – D/A) :
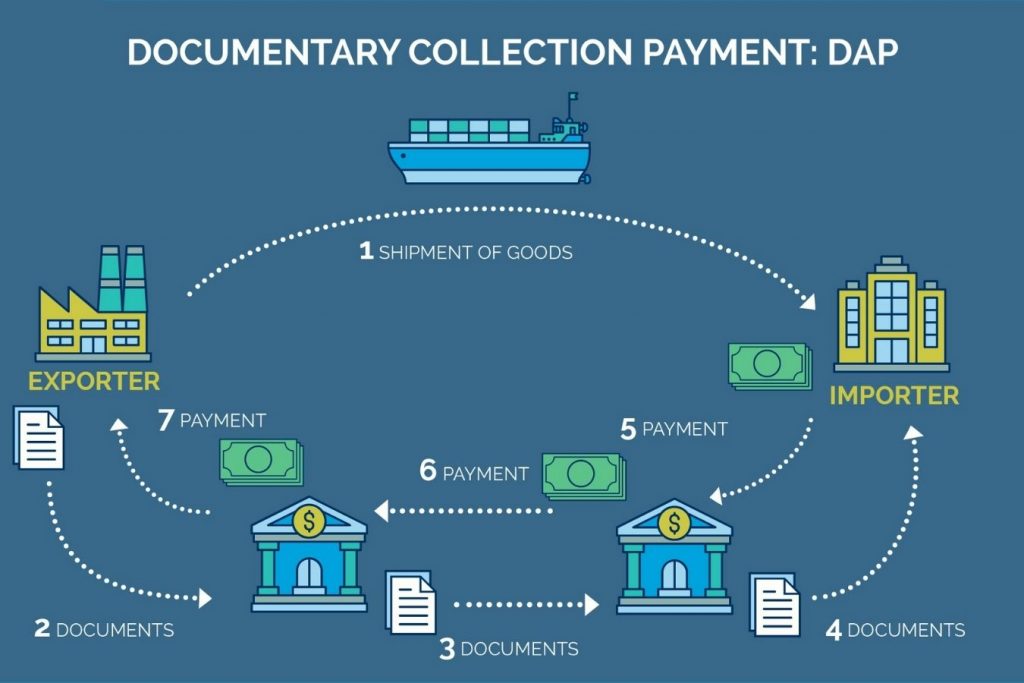
- D/A (Documents against Acceptance) is a condition for accepting payment to exchange documents. The collecting Bank only awards the commercial documents when the importer agrees with the price. For the D/A condition, the collection order must have the directive “Release Documents against Acceptance.”
Process of making payment in exchange for documents:
- Based on the signed commercial contract, the exporter delivers the goods to the importer but does not deliver the goods documents.
- The exporter draws and sends a time bill of exchange, together with collection instructions and a set of goods documents, to the entrusted Bank for collection on behalf of the importer.
- The entrusting Bank transfers the collection instructions and documents to the correspondent bank to notify the importer.
- Based on the collection instruction received, the presenting Bank prepares a notice to the importer.
- If the importer accepts payment by directly taking the bill of exchange or written acceptance, the presenting Bank delivers the goods documents to the importer.
- The presenting bank informs the importer of the payment acceptance to the sending Bank.
- The document transferring Bank notifies the exporter of the result of sending the collection documents under D/A terms to the exporter.
- D/P (Documents against Payment) is a payment condition that pays as soon as the documents are presented (payable at sight). The collecting Bank only awards commercial documents when the importer pays for collection. For D/P conditions, the collection order must contain the instruction “Release Documents against Payment.”
Procedure for accepting payment in exchange for documents:
- Based on the signed commercial contract, the exporter delivers the coffee products to the importer
- The exporter draws and sends the collection instructions with the goods documents (with or without the draft) to the entrusted Bank for collection on behalf of the importer.
- The entrusting Bank transfers the collection instructions and documents to the correspondent bank to notify the importer.
- Based on the collection instruction received, the presenting Bank prepares a notice to the importer.
- The presenting Bank delivers the goods documents to the importer after the importer has transferred sufficient funds for collection payment.
- Presenting Bank pays the collection value to the sending Bank
- The Bank transfers the payment documents to the exporter for collection after deducting service fees and related costs.
- In addition to the two forms of collection of documents under the conditions of D/A and D/P, there are also several conditions for payment for display with other documents, such as:
- Partial payment: Partly according to the value of D/P collection at sight, partly according to the value of D/A collection.
- Deliver documents when there is a promise to pay, a commitment letter, or a trust receipt. In these cases, the payment process is the same as that of D/A, but the Bank only delivers documents when the customer presents a promise to pay, a letter of commitment to pay, or a trust receipt made by the customer himself.
Points to note:
- The Bank is an intermediary to collect money for customers, not responsible for whether the collection is successful.
- The exporter must prepare a collection instruction and send it to the Bank acting on its behalf for collection. The exporter must set forth collection conditions that the collecting Bank must fulfill in the collection instruction.
- If the coffee arrives before the documents, the importer can issue a guarantee with the shipping company to receive the coffee.
- The method of collecting documents ensures the interests of the exporter, the importer who wants to have the coffee must pay money to the exporter’s Bank. However, this method still has many potential risks because the exporter has to waste time and money to recover capital or handle the consignment sent.
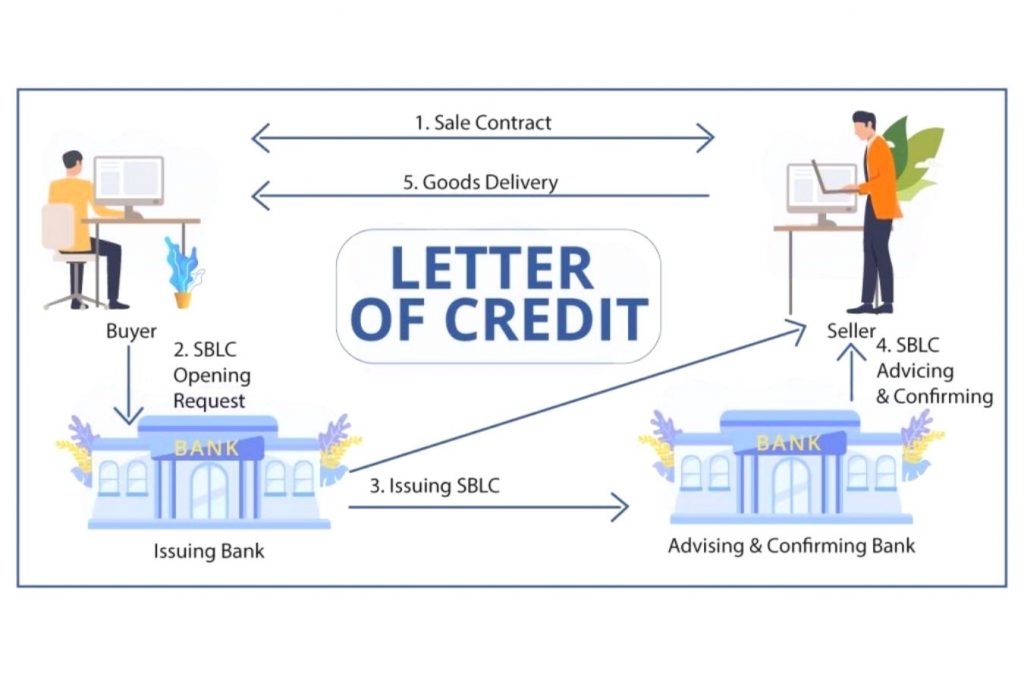
3. Documentary credit payment method – Letter of credit (L/C) in coffee purchasing
Concept:
L/C is understood as a document issued by the importing Bank that commits to paying the exporter after presenting a good set of documents.
Therefore, this L/C is called commercial L/C or documentary L/C. L/C is made based on the contract terms but is entirely independent of the contract.
Characteristic:
L/C is divided into many types as follows:
- Revocable L/C (Revocable L/C)
- Irrevocable Letter of Credit (Irrevocable L/C)
- Confirmed Letter of Credit (Confirmed L/C)
- Transferable L/C
- Back to Back L/C
- Revolving Letter of Credit
- Standby Letter of Credit
- Reciprocal L/C (Reciprocal L/C)
- Red Clause L/C
Participating parties:
- The person who requests the letter of credit: the importer or the importer entrusts another person
- Issuing Bank of the letter of credit: is the Bank in the importer’s country.
- Applicant bank: The branch of the issuing Bank. In Vietnam, the person requesting the issuance of L/C must go through the addition of the Issuing Bank to file a request for L/C issuance. The Issuing Bank entrusts its branch to receive the L/C issuance request.
- Beneficiary: The exporter or any other person nominated by the beneficiary.
- I am advising Bank: The correspondent bank of the issuing bank in the beneficiary’s country.
Main contents required in the L/C:
- Number, location, date of opening L/C
- Type L/C
- Names and addresses of related parties: L/C requesters, beneficiaries, banks…
- Amount, currency
- Validity period, payment term, and delivery term
- Delivery terms: conditions, place of delivery…
- Contents of goods: Scientific name of Coffee, quantity, weight, packaging, packing. …
- The beneficiary must present a draft, commercial invoice, bill of lading, insurance documents, C/0, C/Q…
- The commitment of the Bank to open the letter of credit
- Other content
Procedure for making L/C payment method:
- The exporting party relies on the foreign trade contract to open the L/C at its Bank for the export party to enjoy.
- At the beneficiary’s request, the importing bank issues the L/C and transfers the original L/C to the exporter for the benefit of the exporting Bank (Notifying Bank).
- The representative Bank of the exporter confirms the L/C and returns the original to the exporter.
- Based on the content of the L/C, the exporter delivers the coffee to the importer.
- When delivering the coffee, the exporter completes the documents and sends the draft to the exporting Bank to request payment for that set of documents.
- The notifying Bank that has received the excellent set of documents will carry out payment procedures.
- The advising Bank transfers the payment documents to the importing party’s Bank.
- The importing Bank (L/C Issuing Bank), after receiving the set of documents from the Notifying Bank and checking that it is satisfactory in the L/C, will proceed to transfer the money to the advising Bank.
- The importer’s Bank informs the importer that it has paid the exporter and, at the same time, asks the importer to refund the money; then, it will give the import documents to complete the import procedures.
Points to note:
- The importer who wants the L/C issuing bank must make a written request for the import of L/C to the Bank issuing the L/C in Vietnam.
- Issues of L/C amendments sent from abroad must be notified by the L/C issuing Bank to the importing unit.
- The beneficiary must check the letter of credit.
4. Remittance method – Remittance
Concept:
This is a method where the importing party requests its Bank through an overseas correspondent bank to transfer a certain amount of money to the exporting party.
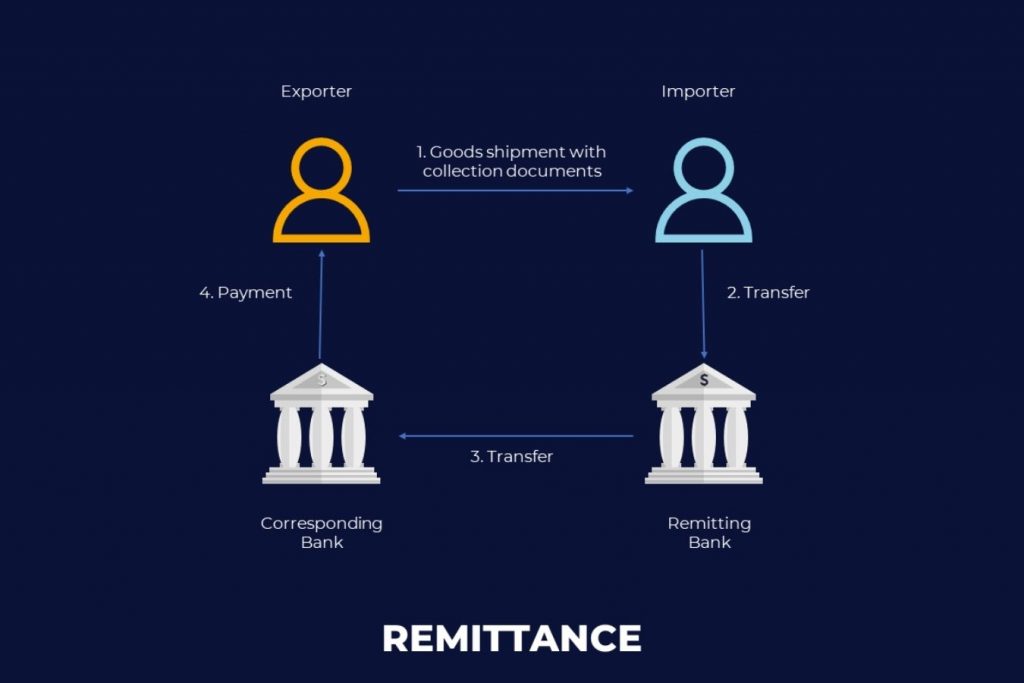
Participating parties:
- Importer – Remitter
- Exporter – Beneficiary
- Importer’s Bank – Remitting Bank
- Exporter’s Bank – Corresponding Bank
Implementation process:
- The importer writes a money transfer request (money order) and sends it to his serving bank, requesting to transfer money to the foreign exporter.
- The remittance bank instructs its correspondent bank in the foreign country to transfer the money and sends a debit note to the importing Bank.
- The importing party’s correspondent bank sends money and a debit note to the exporting party.
- Upon receipt of the payment, the exporter delivers the coffee as requested.
- Before the money is refunded, the money belonging to the remitter has the right to cancel the money transfer order, and the payee has no right to complain.
Current remittance methods:
- Telegraphic Transfer Remittance (T/T): the transfer time is speedy; the remitter must pay the procedure fee and telegram cost. This is the most commonly used method today.
- Mail Transfer Remittance (M/T): long transfer time, low cost.
Points to note:
- The money transfer method is straightforward, low cost (usually only 0.15% – 0.2% of the transferred amount)
- However, this payment method increases the risk for both parties, so it is only applied when there is a reliable trading relationship and the payment value is not significant.
Hopefully, you can better understand the current international payment methods through the above article of Advantage Logistics. Please get in touch with us immediately for specific guidance and advice if you have any questions!
Set of documents in international payment in Coffee Purchasing
A set of documents used in international payments usually includes:
- Commercial invoice
- Transport documents:
- Sea waybill
- Air waybill (Airway bill)
- Multimodal bill of lading…
- Insurance and insurance documents:
- Insurance
- Insurance certificate
- Or the declaration under the insurance contract,…
- Coffee packing slip
- Certificate of Origin
- Other types of certificates:
- Certificate of quantity/weight/quality
- Certificate of animal/plant quarantine,…